Eino ADK: ChatModelAgent
ChatModelAgent Overview
Import Path
import "github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
What is ChatModelAgent
ChatModelAgent is a core prebuilt Agent in Eino ADK. It encapsulates the complex logic of interacting with large language models (LLMs) and supports using tools to accomplish tasks.
ChatModelAgent ReAct Mode
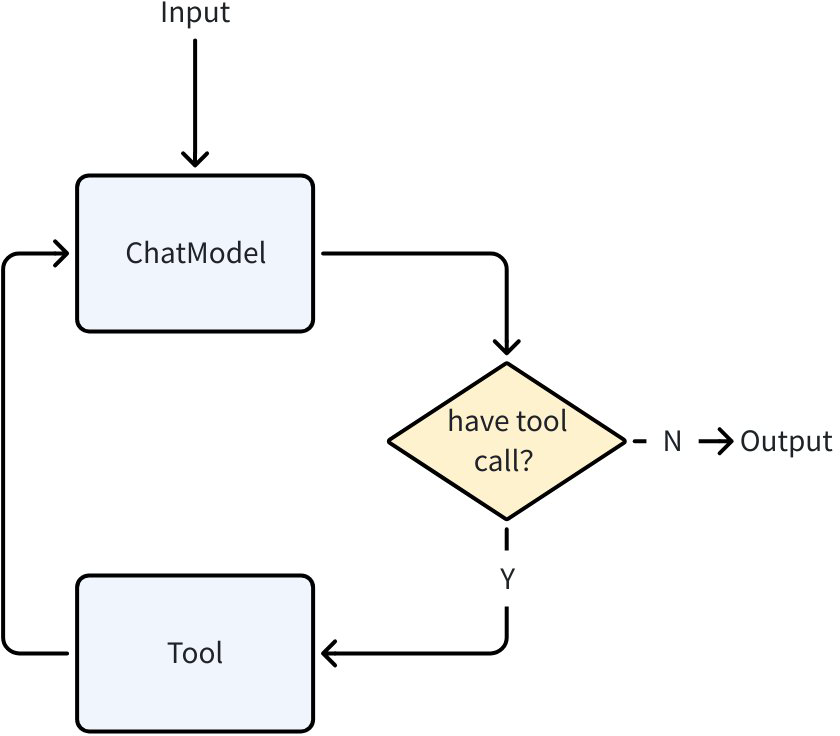
ChatModelAgent uses the ReAct pattern, designed to solve complex problems by letting the ChatModel perform explicit, step-by-step “thinking”. When tools are configured for ChatModelAgent, its internal execution follows the ReAct pattern:
- Call ChatModel (Reason)
- LLM returns a tool-call request (Action)
- ChatModelAgent executes the tool (Act)
- It sends the tool result back to ChatModel (Observation), then starts a new loop until the model decides no tool is needed and stops
When no tools are configured, ChatModelAgent falls back to a single ChatModel call.
Configure tools for ChatModelAgent via ToolsConfig:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/chatmodel.go
type ToolsConfig struct {
compose.ToolsNodeConfig
// Names of the tools that will make agent return directly when the tool is called.
// When multiple tools are called and more than one tool is in the return directly list, only the first one will be returned.
ReturnDirectly map[string]bool
// EmitInternalEvents indicates whether internal events from agentTool should be emitted
// to the parent generator via a tool option injection at run-time.
EmitInternalEvents bool
}
ToolsConfig reuses Eino Graph ToolsNodeConfig. See: Eino: ToolsNode & Tool Guide. Additionally, it provides the ReturnDirectly configuration - ChatModelAgent will exit directly after calling a tool configured in ReturnDirectly.
ChatModelAgent Configuration Fields
💡 Note: By default, GenModelInput renders the Instruction using F-String format via adk.GetSessionValues(). To disable this behavior, you can customize the GenModelInput method.
type ChatModelAgentConfig struct {
// Name of the agent. Better be unique across all agents.
Name string
// Description of the agent's capabilities.
// Helps other agents determine whether to transfer tasks to this agent.
Description string
// Instruction used as the system prompt for this agent.
// Optional. If empty, no system prompt will be used.
// Supports f-string placeholders for session values in default GenModelInput, for example:
// "You are a helpful assistant. The current time is {Time}. The current user is {User}."
// These placeholders will be replaced with session values for "Time" and "User".
Instruction string
Model model.ToolCallingChatModel
ToolsConfig ToolsConfig
// GenModelInput transforms instructions and input messages into the model's input format.
// Optional. Defaults to defaultGenModelInput which combines instruction and messages.
GenModelInput GenModelInput
// Exit defines the tool used to terminate the agent process.
// Optional. If nil, no Exit Action will be generated.
// You can use the provided 'ExitTool' implementation directly.
Exit tool.BaseTool
// OutputKey stores the agent's response in the session.
// Optional. When set, stores output via AddSessionValue(ctx, outputKey, msg.Content).
OutputKey string
// MaxIterations defines the upper limit of ChatModel generation cycles.
// The agent will terminate with an error if this limit is exceeded.
// Optional. Defaults to 20.
MaxIterations int
// ModelRetryConfig configures retry behavior for the ChatModel.
// When set, the agent will automatically retry failed ChatModel calls
// based on the configured policy.
// Optional. If nil, no retry will be performed.
ModelRetryConfig *ModelRetryConfig
}
type ToolsConfig struct {
compose.ToolsNodeConfig
// Names of the tools that will make agent return directly when the tool is called.
// When multiple tools are called and more than one tool is in the return directly list, only the first one will be returned.
ReturnDirectly map[string]bool
// EmitInternalEvents indicates whether internal events from agentTool should be emitted
// to the parent generator via a tool option injection at run-time.
EmitInternalEvents bool
}
type GenModelInput func(ctx context.Context, instruction string, input *AgentInput) ([]Message, error)
Name: Agent nameDescription: Agent descriptionInstruction: System Prompt when calling ChatModel, supports f-string renderingModel: The ChatModel used for execution, must support tool callingToolsConfig: Tool configuration- ToolsConfig reuses Eino Graph ToolsNodeConfig. See: Eino: ToolsNode & Tool Guide.
- ReturnDirectly: After ChatModelAgent calls a tool configured in ReturnDirectly, it will immediately exit with the result without returning to ChatModel in ReAct mode. If multiple tools match, only the first one returns. Map key is the tool name.
- EmitInternalEvents: When using adk.AgentTool() to call an Agent as a SubAgent via ToolCall, by default this SubAgent won’t emit AgentEvents and will only return the final result as ToolResult.
GenModelInput: When the Agent is called, this method transformsInstructionandAgentInputinto Messages for calling ChatModel. The Agent provides a default GenModelInput method:- Prepend
Instructionas aSystem MessagetoAgentInput.Messages - Render
SessionValuesas variables into the message list from step 1
- Prepend
💡 The default
GenModelInputuses pyfmt rendering. Text in the message list is treated as a pyfmt template, meaning ‘{’ and ‘}’ are treated as keywords. To use these characters literally, escape them as ‘{{’ and ‘}}’
OutputKey: When configured, the last Message produced by ChatModelAgent will be stored inSessionValueswithOutputKeyas the keyMaxIterations: Maximum number of ChatModel generations in ReAct mode. The Agent will exit with an error if exceeded. Default is 20Exit: Exit is a special Tool. When the model calls and executes this tool, ChatModelAgent will exit directly, similar toToolsConfig.ReturnDirectly. ADK provides a default ExitTool implementation:
type ExitTool struct{}
func (et ExitTool) Info(_ context.Context) (*schema.ToolInfo, error) {
return ToolInfoExit, nil
}
func (et ExitTool) InvokableRun(ctx context.Context, argumentsInJSON string, _ ...tool.Option) (string, error) {
type exitParams struct {
FinalResult string `json:"final_result"`
}
params := &exitParams{}
err := sonic.UnmarshalString(argumentsInJSON, params)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
err = SendToolGenAction(ctx, "exit", NewExitAction())
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return params.FinalResult, nil
}
ModelRetryConfig: When configured, various errors during ChatModel requests (including direct errors and errors during streaming responses) will be retried according to the configured policy. If an error occurs during streaming response, that streaming response will still be returned immediately via AgentEvent. If the error during streaming will be retried according to the policy, consuming the message stream in AgentEvent will yield aWillRetryError. Users can handle this error for display purposes, as shown below:
iterator := agent.Run(ctx, input)
for {
event, ok := iterator.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
handleFinalError(event.Err)
break
}
// Process streaming output
if event.Output != nil && event.Output.MessageOutput.IsStreaming {
stream := event.Output.MessageOutput.MessageStream
for {
msg, err := stream.Recv()
if err == io.EOF {
break // Stream completed successfully
}
if err != nil {
// Check if this error will be retried (more streams coming)
var willRetry *adk.WillRetryError
if errors.As(err, &willRetry) {
log.Printf("Attempt %d failed, retrying...", willRetry.RetryAttempt)
break // Wait for next event with new stream
}
// Original error - won't retry, agent will stop and the next AgentEvent probably will be an error
log.Printf("Final error (no retry): %v", err)
break
}
// Display chunk to user
displayChunk(msg)
}
}
}
ChatModelAgent Transfer
ChatModelAgent supports converting other Agents’ metadata into its own Tools, enabling dynamic Transfer through ChatModel decisions:
ChatModelAgentimplements theOnSubAgentsinterface. After usingSetSubAgentsto set sub-Agents forChatModelAgent, it adds aTransfer Tooland instructs the ChatModel in the prompt to call this Tool when transfer is needed, using the target AgentName as input.
const (
TransferToAgentInstruction = `Available other agents: %s
Decision rule:
- If you're best suited for the question according to your description: ANSWER
- If another agent is better according its description: CALL '%s' function with their agent name
When transferring: OUTPUT ONLY THE FUNCTION CALL`
)
func genTransferToAgentInstruction(ctx context.Context, agents []Agent) string {
var sb strings.Builder
for _, agent := range agents {
sb.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("\n- Agent name: %s\n Agent description: %s",
agent.Name(ctx), agent.Description(ctx)))
}
return fmt.Sprintf(TransferToAgentInstruction, sb.String(), TransferToAgentToolName)
}
Transfer Toolexecution sets a Transfer Event, specifying the jump to the target Agent, then ChatModelAgent exits.- Agent Runner receives the Transfer Event and jumps to the target Agent for execution, completing the Transfer operation.
ChatModelAgent AgentAsTool
When an Agent to be called doesn’t need the full execution context and only requires clear input parameters to run correctly, that Agent can be converted to a Tool for ChatModelAgent to decide when to call:
- ADK provides utility methods to conveniently convert an Eino ADK Agent to a Tool for ChatModelAgent to call:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/agent_tool.go
func NewAgentTool(_ context.Context, agent Agent, options ...AgentToolOption) tool.BaseTool
- The converted Agent Tool can be registered directly in ChatModelAgent via
ToolsConfig
bookRecommender := NewBookRecommendAgent()
bookRecommendeTool := NewAgentTool(ctx, bookRecommender)
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(ctx, &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
// ...
ToolsConfig: adk.ToolsConfig{
ToolsNodeConfig: compose.ToolsNodeConfig{
Tools: []tool.BaseTool{bookRecommendeTool},
},
},
})
ChatModelAgent Usage Example
Scenario
Create a book recommendation Agent that can recommend relevant books based on user input.
Implementation
Step 1: Define the Tool
The book recommendation Agent needs a tool book_search that can search for books based on user requirements (genre, rating, etc.).
You can easily create tools using the utility methods provided by Eino (see How to Create a Tool?):
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool/utils"
)
type BookSearchInput struct {
Genre string `json:"genre" jsonschema:"description=Preferred book genre,enum=fiction,enum=sci-fi,enum=mystery,enum=biography,enum=business"`
MaxPages int `json:"max_pages" jsonschema:"description=Maximum page length (0 for no limit)"`
MinRating int `json:"min_rating" jsonschema:"description=Minimum user rating (0-5 scale)"`
}
type BookSearchOutput struct {
Books []string
}
func NewBookRecommender() tool.InvokableTool {
bookSearchTool, err := utils.InferTool("search_book", "Search books based on user preferences", func(ctx context.Context, input *BookSearchInput) (output *BookSearchOutput, err error) {
// search code
// ...
return &BookSearchOutput{Books: []string{"God's blessing on this wonderful world!"}}, nil
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to create search book tool: %v", err)
}
return bookSearchTool
}
Step 2: Create ChatModel
Eino provides various ChatModel implementations (such as openai, gemini, doubao, etc. See Eino: ChatModel Guide). Here we use openai ChatModel as an example:
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-ext/components/model/openai"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/model"
)
func NewChatModel() model.ToolCallingChatModel {
ctx := context.Background()
apiKey := os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
openaiModel := os.Getenv("OPENAI_MODEL")
cm, err := openai.NewChatModel(ctx, &openai.ChatModelConfig{
APIKey: apiKey,
Model: openaiModel,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(fmt.Errorf("failed to create chatmodel: %w", err))
}
return cm
}
Step 3: Create ChatModelAgent
In addition to configuring ChatModel and tools, you need to configure Name and Description to describe the Agent’s functionality, as well as Instruction to guide the ChatModel. The Instruction will ultimately be passed to ChatModel as a system message.
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose"
)
func NewBookRecommendAgent() adk.Agent {
ctx := context.Background()
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(ctx, &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
Name: "BookRecommender",
Description: "An agent that can recommend books",
Instruction: `You are an expert book recommender. Based on the user's request, use the "search_book" tool to find relevant books. Finally, present the results to the user.`,
Model: NewChatModel(),
ToolsConfig: adk.ToolsConfig{
ToolsNodeConfig: compose.ToolsNodeConfig{
Tools: []tool.BaseTool{NewBookRecommender()},
},
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(fmt.Errorf("failed to create chatmodel: %w", err))
}
return a
}
Step 4: Run via Runner
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino-examples/adk/intro/chatmodel/internal"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
a := internal.NewBookRecommendAgent()
runner := adk.NewRunner(ctx, adk.RunnerConfig{
Agent: a,
})
iter := runner.Query(ctx, "recommend a fiction book to me")
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
log.Fatal(event.Err)
}
msg, err := event.Output.MessageOutput.GetMessage()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("\nmessage:\n%v\n======", msg)
}
}
Run Result
message:
assistant:
tool_calls:
{Index:<nil> ID:call_o2It087hoqj8L7atzr70EnfG Type:function Function:{Name:search_book Arguments:{"genre":"fiction","max_pages":0,"min_rating":0}} Extra:map[]}
finish_reason: tool_calls
usage: &{140 24 164}
======
message:
tool: {"Books":["God's blessing on this wonderful world!"]}
tool_call_id: call_o2It087hoqj8L7atzr70EnfG
tool_call_name: search_book
======
message:
assistant: I recommend the fiction book "God's blessing on this wonderful world!". It's a great choice for readers looking for an exciting story. Enjoy your reading!
finish_reason: stop
usage: &{185 31 216}
======
ChatModelAgent Interrupt & Resume
Introduction
ChatModelAgent is implemented using Eino Graph, so the agent can reuse Eino Graph’s Interrupt & Resume capability.
- On interrupt, return a special error from the tool to trigger Graph interrupt and emit custom info. On resume, Graph will rerun this tool:
// github.com/cloudwego/eino/adk/interrupt.go
func NewInterruptAndRerunErr(extra any) error
- On resume, support custom ToolOptions to pass extra information to the Tool:
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool"
)
type askForClarificationOptions struct {
NewInput *string
}
func WithNewInput(input string) tool.Option {
return tool.WrapImplSpecificOptFn(func(t *askForClarificationOptions) {
t.NewInput = &input
})
}
Example
Below we will add an ask_for_clarification tool to the BookRecommendAgent from the [ChatModelAgent Usage Example] section above. When the user provides insufficient information for recommendations, the Agent will call this tool to ask the user for more information. ask_for_clarification uses the Interrupt & Resume capability to implement “asking” the user.
Step 1: Add Tool with Interrupt Support
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/components/tool/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/eino/compose"
)
type askForClarificationOptions struct {
NewInput *string
}
func WithNewInput(input string) tool.Option {
return tool.WrapImplSpecificOptFn(func(t *askForClarificationOptions) {
t.NewInput = &input
})
}
type AskForClarificationInput struct {
Question string `json:"question" jsonschema:"description=The specific question you want to ask the user to get the missing information"`
}
func NewAskForClarificationTool() tool.InvokableTool {
t, err := utils.InferOptionableTool(
"ask_for_clarification",
"Call this tool when the user's request is ambiguous or lacks the necessary information to proceed. Use it to ask a follow-up question to get the details you need, such as the book's genre, before you can use other tools effectively.",
func(ctx context.Context, input *AskForClarificationInput, opts ...tool.Option) (output string, err error) {
o := tool.GetImplSpecificOptions[askForClarificationOptions](nil, opts...)
if o.NewInput == nil {
return "", compose.NewInterruptAndRerunErr(input.Question)
}
return *o.NewInput, nil
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return t
}
Step 2: Add Tool to Agent
func NewBookRecommendAgent() adk.Agent {
// xxx
a, err := adk.NewChatModelAgent(ctx, &adk.ChatModelAgentConfig{
// xxx
ToolsConfig: adk.ToolsConfig{
ToolsNodeConfig: compose.ToolsNodeConfig{
Tools: []tool.BaseTool{NewBookRecommender(), NewAskForClarificationTool()},
},
// Whether to output AgentEvents when calling SubAgent via AgentTool() internally
EmitInternalEvents: true,
},
})
// xxx
}
Step 3: Configure CheckPointStore in Agent Runner
Configure CheckPointStore in the Runner (using the simplest InMemoryStore in this example), and pass CheckPointID when calling the Agent for use during resume. Also, on interrupt, Graph will place InterruptInfo in Interrupted.Data:
func newInMemoryStore() compose.CheckPointStore {
return &inMemoryStore{
mem: map[string][]byte{},
}
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
a := subagents.NewBookRecommendAgent()
runner := adk.NewRunner(ctx, adk.RunnerConfig{
EnableStreaming: true, // you can disable streaming here
Agent: a,
CheckPointStore: newInMemoryStore(),
})
iter := runner.Query(ctx, "recommend a book to me", adk.WithCheckPointID("1"))
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
log.Fatal(event.Err)
}
if event.Action != nil && event.Action.Interrupted != nil {
fmt.Printf("\ninterrupt happened, info: %+v\n", event.Action.Interrupted.Data.(*adk.ChatModelAgentInterruptInfo).RerunNodesExtra["ToolNode"])
continue
}
msg, err := event.Output.MessageOutput.GetMessage()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("\nmessage:\n%v\n======\n\n", msg)
}
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(os.Stdin)
fmt.Print("\nyour input here: ")
scanner.Scan()
fmt.Println()
nInput := scanner.Text()
iter, err := runner.Resume(ctx, "1", adk.WithToolOptions([]tool.Option{subagents.WithNewInput(nInput)}))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
for {
event, ok := iter.Next()
if !ok {
break
}
if event.Err != nil {
log.Fatal(event.Err)
}
prints.Event(event)
}
}
Run Result
Running will trigger an interrupt
message:
assistant:
tool_calls:
{Index:<nil> ID:call_3HAobzkJvW3JsTmSHSBRftaG Type:function Function:{Name:ask_for_clarification Arguments:{"question":"Could you please specify the genre you're interested in and any preferences like maximum page length or minimum user rating?"}} Extra:map[]}
finish_reason: tool_calls
usage: &{219 37 256}
======
interrupt happened, info: &{ToolCalls:[{Index:<nil> ID:call_3HAobzkJvW3JsTmSHSBRftaG Type:function Function:{Name:ask_for_clarification Arguments:{"question":"Could you please specify the genre you're interested in and any preferences like maximum page length or minimum user rating?"}} Extra:map[]}] ExecutedTools:map[] RerunTools:[call_3HAobzkJvW3JsTmSHSBRftaG] RerunExtraMap:map[call_3HAobzkJvW3JsTmSHSBRftaG:Could you please specify the genre you're interested in and any preferences like maximum page length or minimum user rating?]}
your input here:
After stdin input, retrieve the previous interrupt state from CheckPointStore, combine with the completed input, and continue running
new input is:
recommend me a fiction book
message:
tool: recommend me a fiction book
tool_call_id: call_3HAobzkJvW3JsTmSHSBRftaG
tool_call_name: ask_for_clarification
======
message:
assistant:
tool_calls:
{Index:<nil> ID:call_3fC5OqPZLls11epXMv7sZGAF Type:function Function:{Name:search_book Arguments:{"genre":"fiction","max_pages":0,"min_rating":0}} Extra:map[]}
finish_reason: tool_calls
usage: &{272 24 296}
======
message:
tool: {"Books":["God's blessing on this wonderful world!"]}
tool_call_id: call_3fC5OqPZLls11epXMv7sZGAF
tool_call_name: search_book
======
message:
assistant: I recommend the fiction book "God's Blessing on This Wonderful World!" Enjoy your reading!
finish_reason: stop
usage: &{317 20 337}
======
Summary
ChatModelAgent is the core Agent implementation in ADK, serving as the “thinking” part of applications. It leverages the powerful capabilities of LLMs for reasoning, understanding natural language, making decisions, generating responses, and interacting with tools.
ChatModelAgent’s behavior is non-deterministic, dynamically deciding which tools to use or transferring control to other Agents through the LLM.