Eino ADK: Quickstart
Installation
Eino provides ADK from v0.5.0. Upgrade your project:
// stable >= eino@v0.5.0
go get github.com/cloudwego/eino@latest
Agent
What is Eino ADK
Eino ADK, inspired by Google‑ADK, is a Go framework for building Agent and Multi‑Agent applications. It standardizes context passing, event streaming, task transfer, interrupts/resume, and cross‑cutting features.
What is an Agent
An Agent is the core of Eino ADK, representing an independent, executable intelligent task unit. You can think of it as an “intelligent entity” that can understand instructions, execute tasks, and provide responses. Each Agent has a clear name and description, making it discoverable and callable by other Agents.
Any scenario requiring interaction with a Large Language Model (LLM) can be abstracted as an Agent. For example:
- An Agent for querying weather information
- An Agent for booking meetings
- An Agent capable of answering domain‑specific questions
Agent in ADK
All features in Eino ADK are designed around the Agent abstraction:
type Agent interface {
Name(ctx context.Context) string
Description(ctx context.Context) string
Run(ctx context.Context, input *AgentInput) *AsyncIterator[*AgentEvent]
}
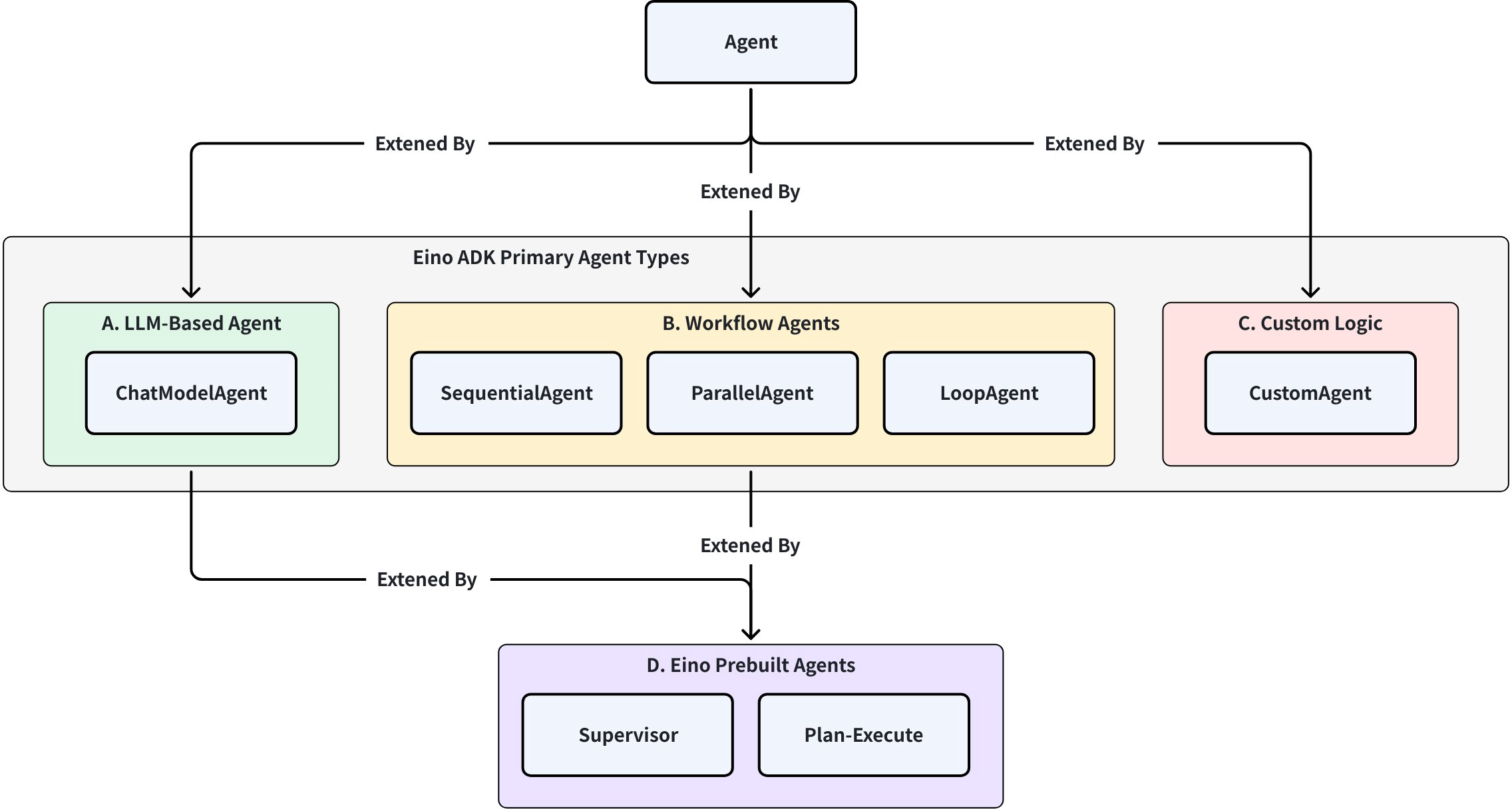
Based on the Agent abstraction, ADK provides three base extension categories:
ChatModel Agent: The “thinking” part of the application, using LLM as its core to understand natural language, perform reasoning, planning, generate responses, and dynamically decide how to execute or which tools to use.Workflow Agents: The coordination and management part of the application, controlling sub-Agent execution flow based on predefined logic according to their type (sequential/parallel/loop). Workflow Agents produce deterministic, predictable execution patterns, unlike the dynamic random decisions generated by ChatModel Agent.- Sequential (Sequential Agent): Execute sub-Agents in order
- Loop (Loop Agent): Repeatedly execute sub-Agents until a specific termination condition is met
- Parallel (Parallel Agent): Execute multiple sub-Agents concurrently
Custom Agent: Implement your own Agent through the interface, allowing highly customized complex Agents
Based on these base extensions, you can combine these basic Agents according to your needs to build the Multi-Agent system you require. Additionally, Eino provides several out-of-the-box Multi-Agent best practice paradigms based on daily practical experience:
- Supervisor: Supervisor mode, where the Supervisor Agent controls all communication flows and task delegation, deciding which Agent to call based on current context and task requirements.
- Plan-Execute: Plan-Execute mode, where the Plan Agent generates a plan with multiple steps, and the Execute Agent completes tasks based on user query and the plan. After execution, Plan is called again to decide whether to complete the task or replan.
The table and diagram below provide the characteristics, differences, and relationships of these base extensions and encapsulations. Subsequent chapters will detail the principles and specifics of each type:
| Category | ChatModel Agent | Workflow Agents | Custom Logic | EinoBuiltInAgent (supervisor, plan‑execute) |
| Function | Thinking, generation, tool calls | Control execution flow among agents | Run custom logic | Out‑of‑the‑box multi‑agent pattern encapsulation |
| Core | LLM | Predetermined execution flows (sequential/parallel/loop) | Custom code | High‑level encapsulation based on Eino practical experience |
| Purpose | Generation, dynamic decisions | Structured processing, orchestration | Customization needs | Turnkey solutions for specific scenarios |
ADK Examples
The Eino‑examples project provides various ADK implementation examples. You can refer to the example code and descriptions to build an initial understanding of ADK capabilities:
| Project Path | Introduction | Diagram |
| Sequential workflow example | This example code demonstrates a sequential multi-agent workflow built using Eino ADK's Workflow paradigm. | 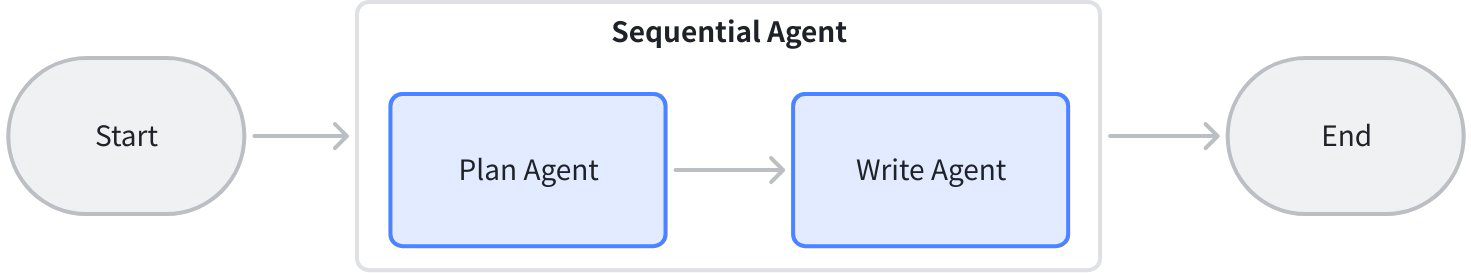 |
| Loop workflow example | This example code builds a reflection-iteration agent framework based on Eino ADK's Workflow paradigm using LoopAgent. | 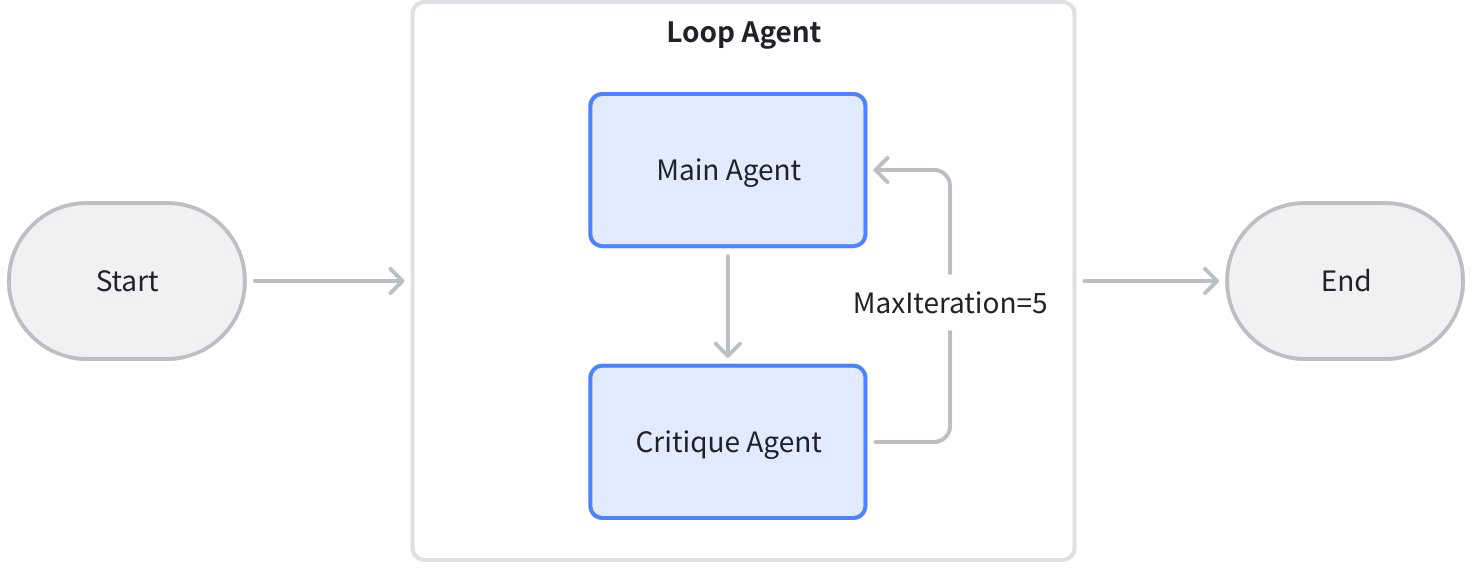 |
| Parallel workflow example | This example code builds a concurrent information collection framework based on Eino ADK's Workflow paradigm using ParallelAgent: | 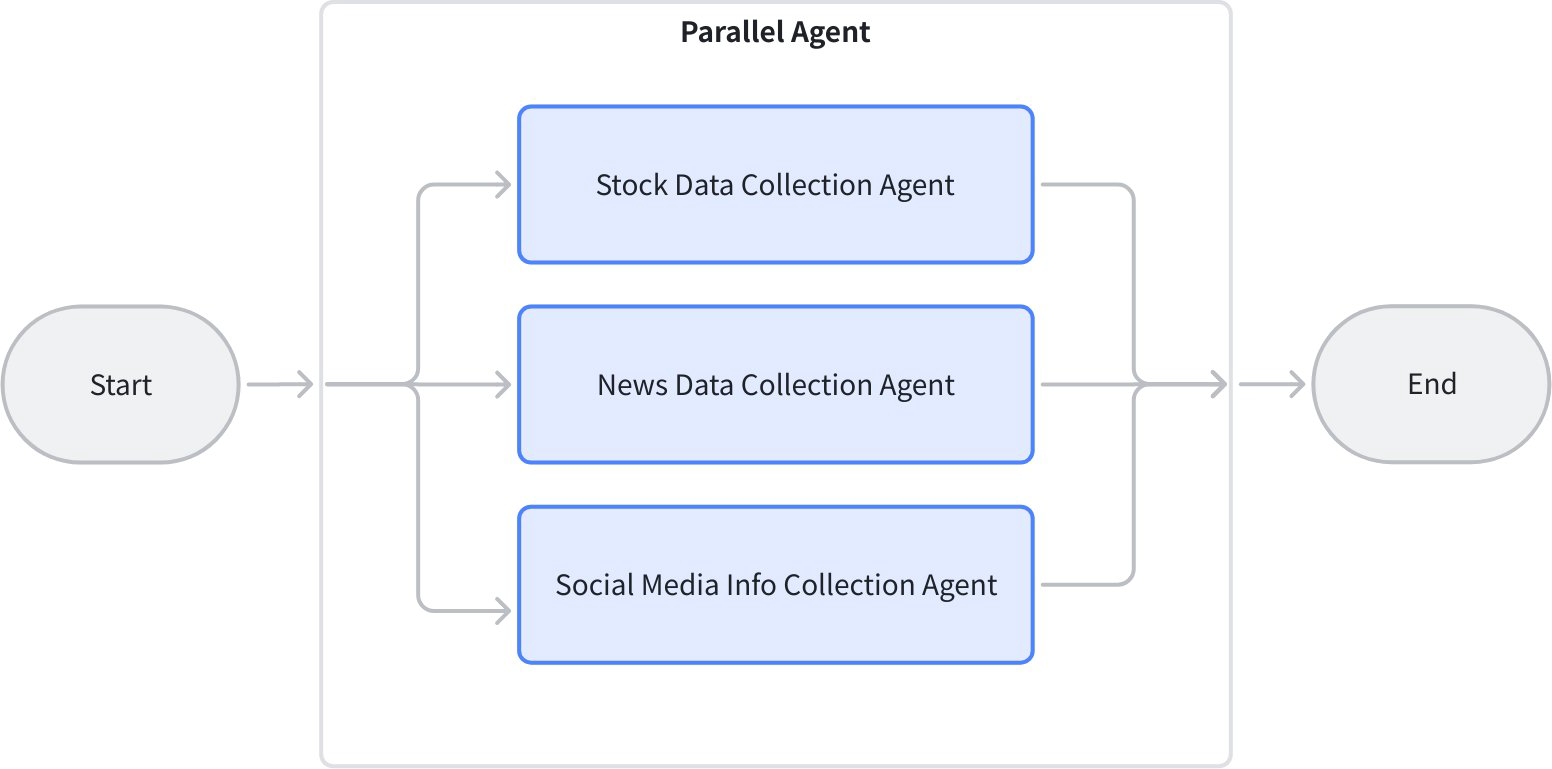 |
| supervisor | This use case employs a single-layer Supervisor managing two relatively comprehensive sub-Agents: Research Agent handles retrieval tasks, Math Agent handles various mathematical operations (add, multiply, divide), but all math operations are uniformly processed within the same Math Agent rather than being split into multiple sub-Agents. This design simplifies the agent hierarchy, suitable for scenarios where tasks are relatively concentrated and don't require excessive decomposition, facilitating rapid deployment and maintenance. | 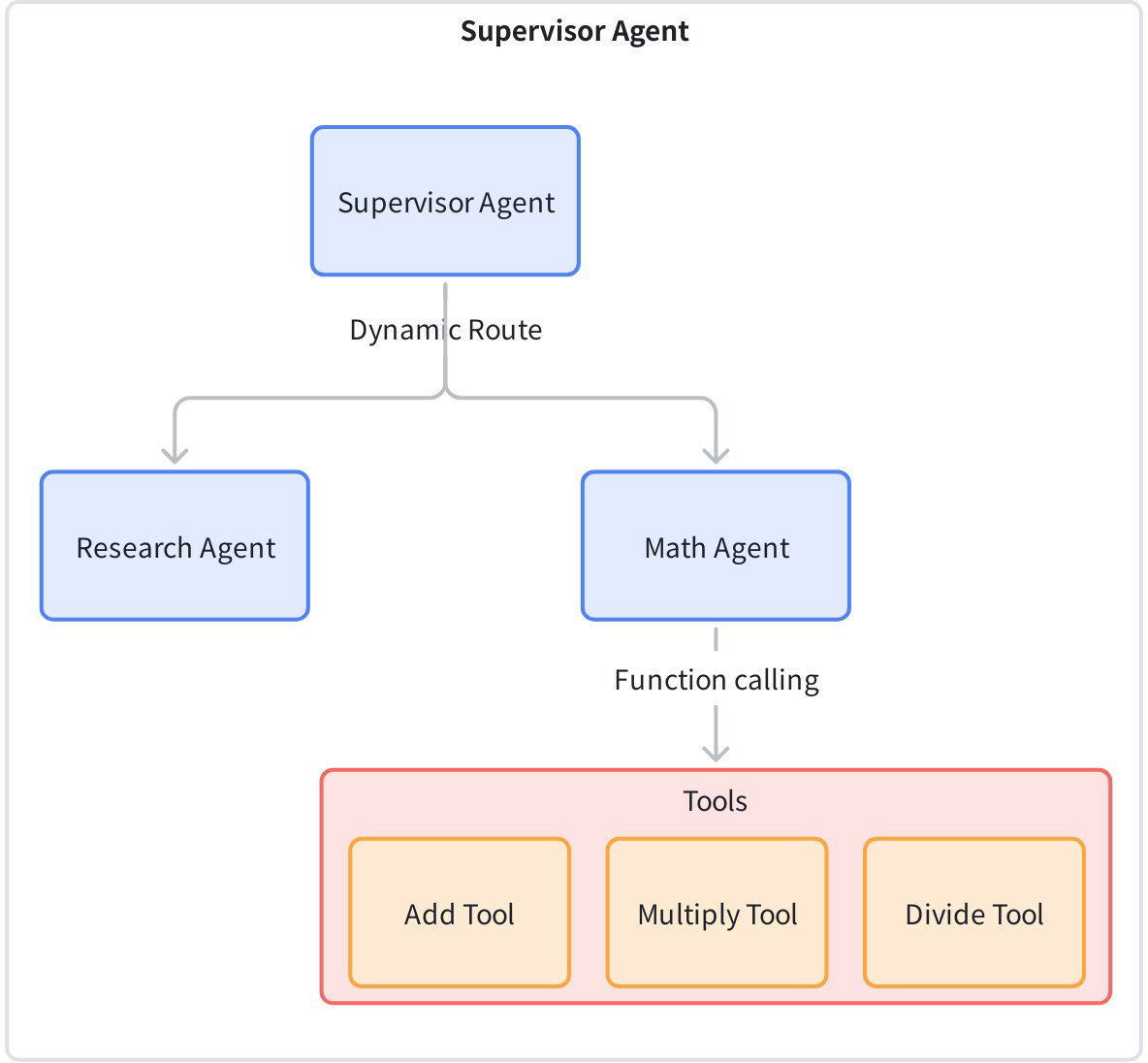 |
| layered‑supervisor | This use case implements a multi-tier intelligent agent supervision system, where the top-level Supervisor manages Research Agent and Math Agent, and Math Agent is further subdivided into three sub-Agents: Subtract, Multiply, and Divide. The top-level Supervisor is responsible for assigning research tasks and math tasks to lower-level Agents, while Math Agent as a mid-tier supervisor further dispatches specific math operation tasks to its sub-Agents. | 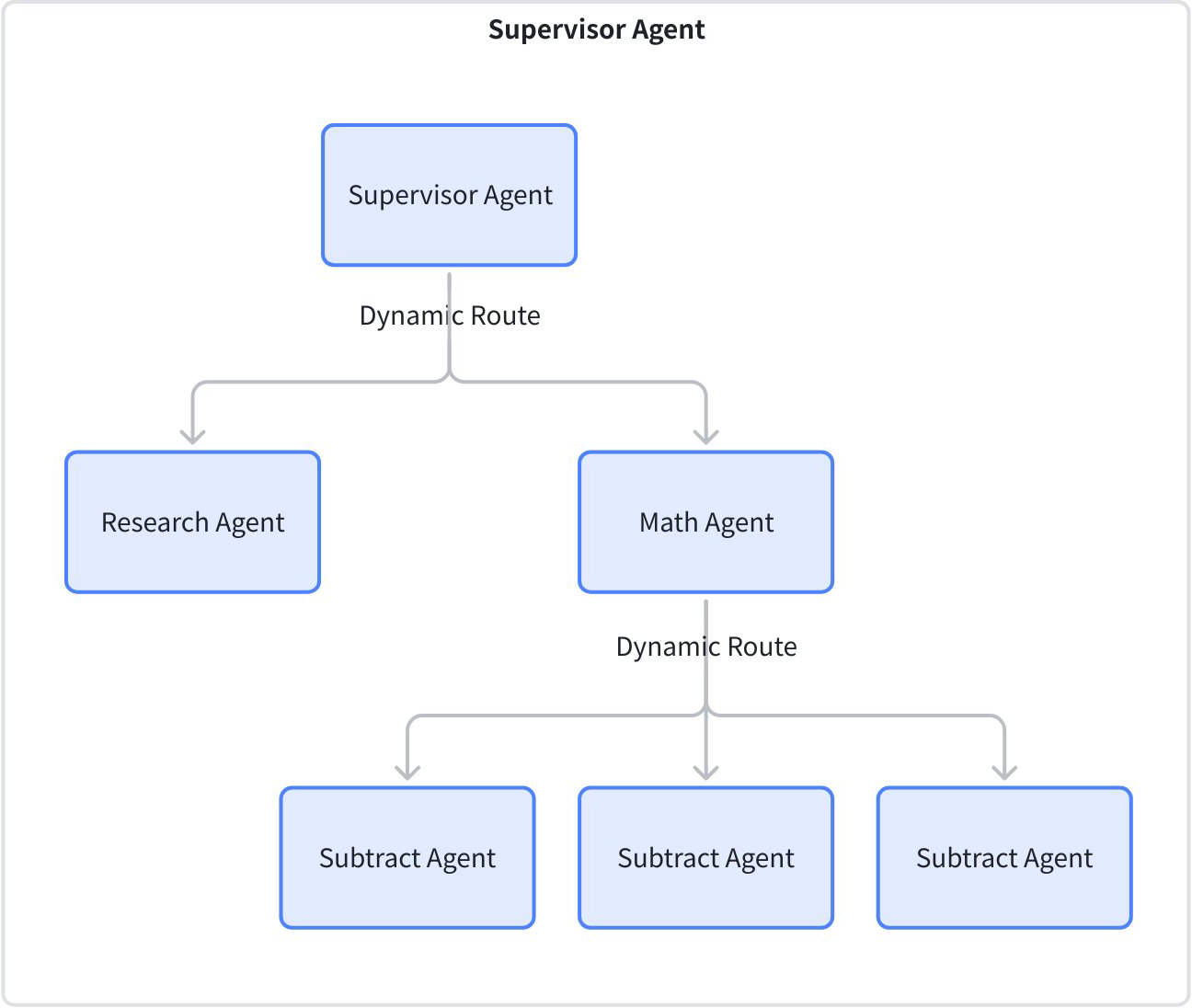 |
| plan‑execute example | This example implements a multi-Agent travel planning system using the plan-execute-replan pattern based on Eino ADK. The core function is to process complex user travel requests (such as "3-day Beijing trip, need flights from New York, hotel recommendations, must-see attractions") through a "plan-execute-replan" loop to complete tasks: 1. Plan: Planner Agentgenerates a step-by-step execution plan based on the large model (e.g., "Step 1: check Beijing weather, Step 2: search New York to Beijing flights"); 2. Execute: Executor Agentcalls mock tools **weather (get_weather), flights (search_flights), hotels (search_hotels), attractions (search_attractions)** to execute each step. If user input information is missing (e.g., budget not specified), it calls ask_for_clarificationtool to ask follow-up questions; 3. Replan: Replanner Agentevaluates whether the plan needs adjustment based on tool execution results (e.g., if no flight tickets available, reselect dates). Execute and Replan continuously loop until all steps in the plan are completed; 4. Supports session trajectory tracking (CozeLoop callback) and state management, ultimately outputting a complete travel plan. Structurally, plan-execute-replan has two layers: | 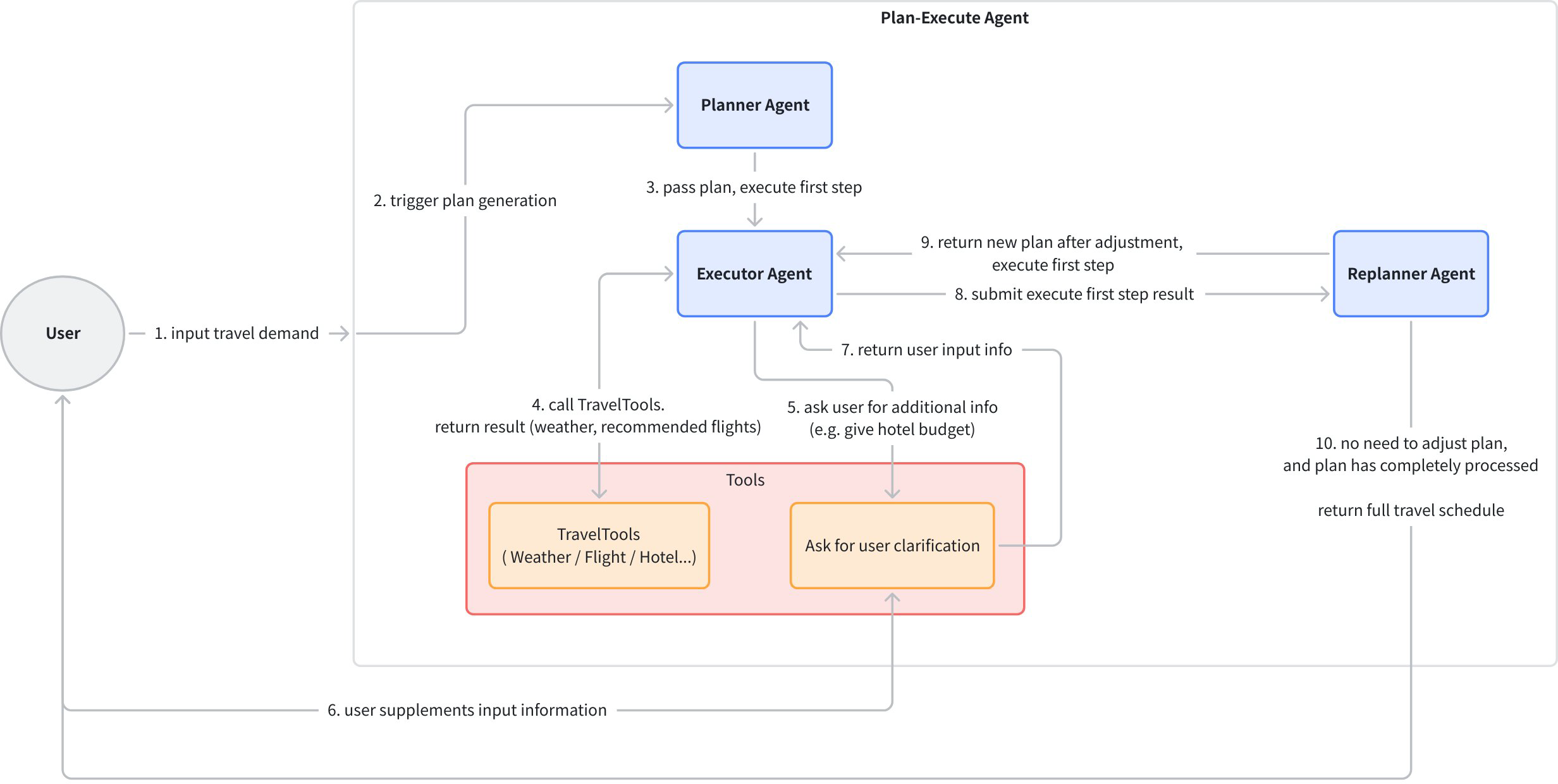 |
| book recommendation agent (interrupt and resume) | This code demonstrates a book recommendation chat agent implementation built on the Eino ADK framework, showcasing Agent interrupt and resume functionality. | 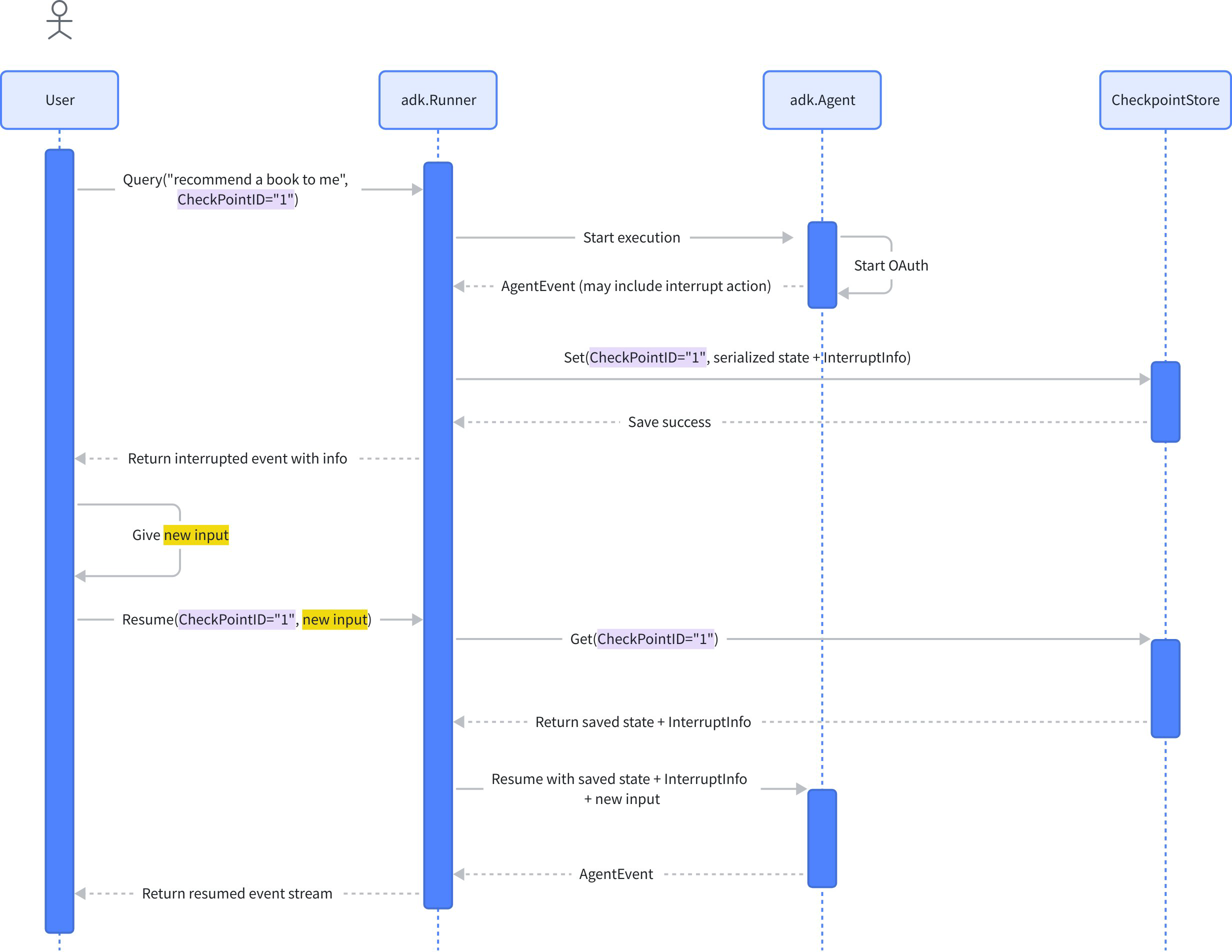 |
What’s Next
After this Quickstart overview, you should have a basic understanding of Eino ADK and Agents.
The following articles will dive deep into ADK core concepts to help you understand how Eino ADK works and use it more effectively: